Abell 520
| RA | Dec | z |
|---|---|---|
| 04:54:19.0 | +02:56:49 | 0.201 |
Summary
Summary (work in progress)
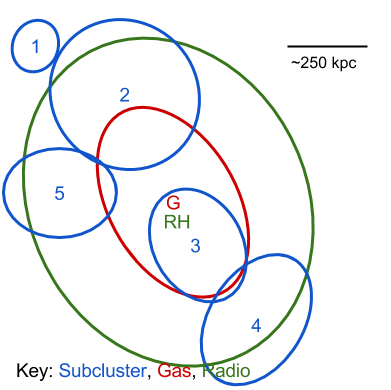
Abell 520 was identified as a radio halo candidate by Giovannini et al. (1999). Govoni et al. (2001) later confirmed this and noted that the radio halo is elongated in the NE-SW direction (which corresponds to the primary merger axis). They also identified two head-tail radio galaxies in the west with their tails pointed away from the cluster center.
Radio references:
Vacca et al. (2013) have a nice literature review.
Govoni et al (2001)... radio halo elongated along merger direction, two head tail radio cluster members, ROSAT X-ray analysis
Giovannini et al (1999)
X-ray:
Govoni et al. (2001)
Optical:
Proust et al. (2000) redshift survey
Lensing references:
Mahdavi et al 2007
Jee et al 2014
Abell 520 was identified as a radio halo candidate by Giovannini et al. (1999). Govoni et al. (2001) later confirmed this and noted that the radio halo is elongated in the NE-SW direction (which corresponds to the primary merger axis). They also identified two head-tail radio galaxies in the west with their tails pointed away from the cluster center.
Radio references:
Vacca et al. (2013) have a nice literature review.
Govoni et al (2001)... radio halo elongated along merger direction, two head tail radio cluster members, ROSAT X-ray analysis
Giovannini et al (1999)
X-ray:
Govoni et al. (2001)
Optical:
Proust et al. (2000) redshift survey
Lensing references:
Mahdavi et al 2007
Jee et al 2014
Existing Data
|
Optical Imaging
|
Spectra
|
X-ray
|
Radio
|
Gallery
References
- Giovannini, G., Tordi, M. & Feretti, L., 1999. Radio halo and relic candidates from the NRAO VLA Sky Survey. New Astronomy, 4(2), pp.141–155.
- Proust, D. et al., 2000. Dynamics of the X-ray clusters Abell 222, Abell 223 and Abell 520. Astronomy and Astrophysics, 355, pp.443–453.
- Govoni, F. et al., 2001. Radio and X-ray diffuse emission in six clusters of galaxies. Astronomy and Astrophysics, 376(03), pp.803–819.
- Govoni, F. et al., 2004. ChandraTemperature Maps for Galaxy Clusters with Radio Halos. The Astrophysical Journal, 605(2), pp.695–708.
- Markevitch, M. et al., 2005. Bow Shock and Radio Halo in the Merging Cluster A520. The Astrophysical Journal, 627(2), pp.733–738.
- Mahdavi, A. et al., 2007. A Dark Core in Abell 520. The Astrophysical Journal, 668(2), pp.806–814.
- Okabe, N. & Umetsu, K., 2008. Subaru Weak Lensing Study of Seven Merging Clusters: Distributions of Mass and Baryons. Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan, 60, pp.345–.
- Girardi, M. et al., 2008. Cluster Abell 520: a perspective based on member galaxies. Astronomy and Astrophysics, 491(2), pp.379–395.
- Jee, M.J. et al., 2012. A STUDY OF THE DARK CORE IN A520 WITH THE HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE: THE MYSTERY DEEPENS. The Astrophysical Journal, 747(2), p.96.
- Clowe, D. et al., 2012. ON DARK PEAKS AND MISSING MASS: A WEAK-LENSING MASS RECONSTRUCTION OF THE MERGING CLUSTER SYSTEM A520. The Astrophysical Journal, 758(2), p.128.
- Jee, M.J. et al., 2013. Hubble Space Telescope/Advanced Camera for Surveys Confirmation of the Dark Substructure in A520. eprint arXiv:1401.3356.
- Vacca, V. et al., 2013. Spectral index image of the radio halo in the cluster Abell 520, which hosts the famous bow shock. Astronomy and Astrophysics, 561, p.A52.
* Lensing quality imaging
^ Galaxies with spectroscopic redshifts near the cluster within a radius of 2 Mpc of the system center.
^ Galaxies with spectroscopic redshifts near the cluster within a radius of 2 Mpc of the system center.